Camera for Quasars in the Early Universe
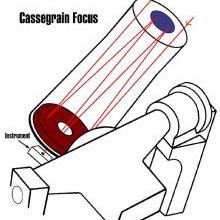 Light from the primary mirror is reflected by a secondary mirror to an instument attached to the telescope through a hole in the primary mirror.
The Camera for Quasars in the Early Universe (CQUEAN) is a multipurpose imaging camera located at the Cassegrain focus of the Otto Struve Telescope. It is optimized for viewing red objects that emit wavelengths between 0.7 to 1.1 microns. Its field of view is fairly large for professional-grade telescopes, at 4.7 sqaure arcminutes.
Light from the primary mirror is reflected by a secondary mirror to an instument attached to the telescope through a hole in the primary mirror.
The Camera for Quasars in the Early Universe (CQUEAN) is a multipurpose imaging camera located at the Cassegrain focus of the Otto Struve Telescope. It is optimized for viewing red objects that emit wavelengths between 0.7 to 1.1 microns. Its field of view is fairly large for professional-grade telescopes, at 4.7 sqaure arcminutes.
The instrument has a fast readout time that allows for astronomers to observe celestial objects whose light output varies rapidly. CQUEAN also includes an auto-guider program to keep the telescope tracking an object across the sky during long exposure times.
"The red sensitivity and no fringing at long wavelengths make the camera special, "Dr. Myungshin Im, from Seoul National University, co-Principal Investigator of the CQUEAN project explains. "We wanted to obtain imaging data to select high-redshift quasars. Usually quasars have red colors due to their spectra being red-shifted to longer wavelengths. This requirement called for a construction of a red-sensitive imager, and to be competitive with other surveys, we built CQUEAN quickly with off-the-shelf components."
CQUEAN is good at detecting red wavelengths because it has a CCD designed to work well at long wavelengths.The trade-off is that to gain efficiency in the red part of the spectrum, it must lose efficiency in the blue. Currently, the CQUEAN team is working to improve the sensitivity at blue wavelengths by replacing some of the optics in the system.
CQUEAN was constructed at Kyunghee University and Seoul National University of Korea from February 2009 through August 2010. Dr. Im and Professor Soojong Pak (Kyunghee University) are the leaders of the CQUEAN project. Dr. Won-Kee Park (Seoul National University) was in charge of software development. Dr. Seunghyuk Jang (Samsung) was responsible for the optical design of the focal reducer. Also, students at Kyunghee University and Seoul National University worked on the development of the camera.
CQUEAN has been used to select 20 high redshift quasar candidates for spectroscopic follow up in the Infrared Multi-tiered Survey. It also obtained images of a supernova in the M101 galaxy. The CQUEAN team is also working on CQUEAN2, a similar camera with a field of view nearly 100 times larger.


